Glossary
Top 10 Privileged Access Management Use Cases to Implement
Explore Procyon’s top 10 Privileged Access Management use cases for securing credentials, controlling access, and ensuring compliance in cybersecurity.

Table of Content
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a cybersecurity framework that controls and monitors access to critical systems and sensitive information. This particular level of access goes beyond what standard users have, enabling the management of critical infrastructure, applications, and sensitive data. PAM encompasses a combination of people, processes, and technology to oversee and regulate all privileged identities, whether human or machine.
All PAM strategies are built around the principle of least privilege, which restricts users to the minimum level of access necessary for their roles. This principle helps reduce the attack surface and minimizes internal and external risks. PAM also involves monitoring and auditing privileged activities to quickly detect and respond to malicious actions.
PAM is critical due to the significant risks associated with privileged access. People are often the weakest point, prone to misusing their privileges or falling victim to credential theft. Additionally, with the rise of digital business, cloud computing, and automation, the number of non-human entities requiring privileged access has surged, complicating management and increasing potential vulnerabilities.
Key Components and Benefits of PAM
PAM adopts a holistic approach, integrating people, processes, and technology to manage and monitor privileged accounts. This approach is relevant for both human users and non-human entities, like applications and machine identities, which need privileged access to function within the enterprise environment.
Critical aspects of PAM include:
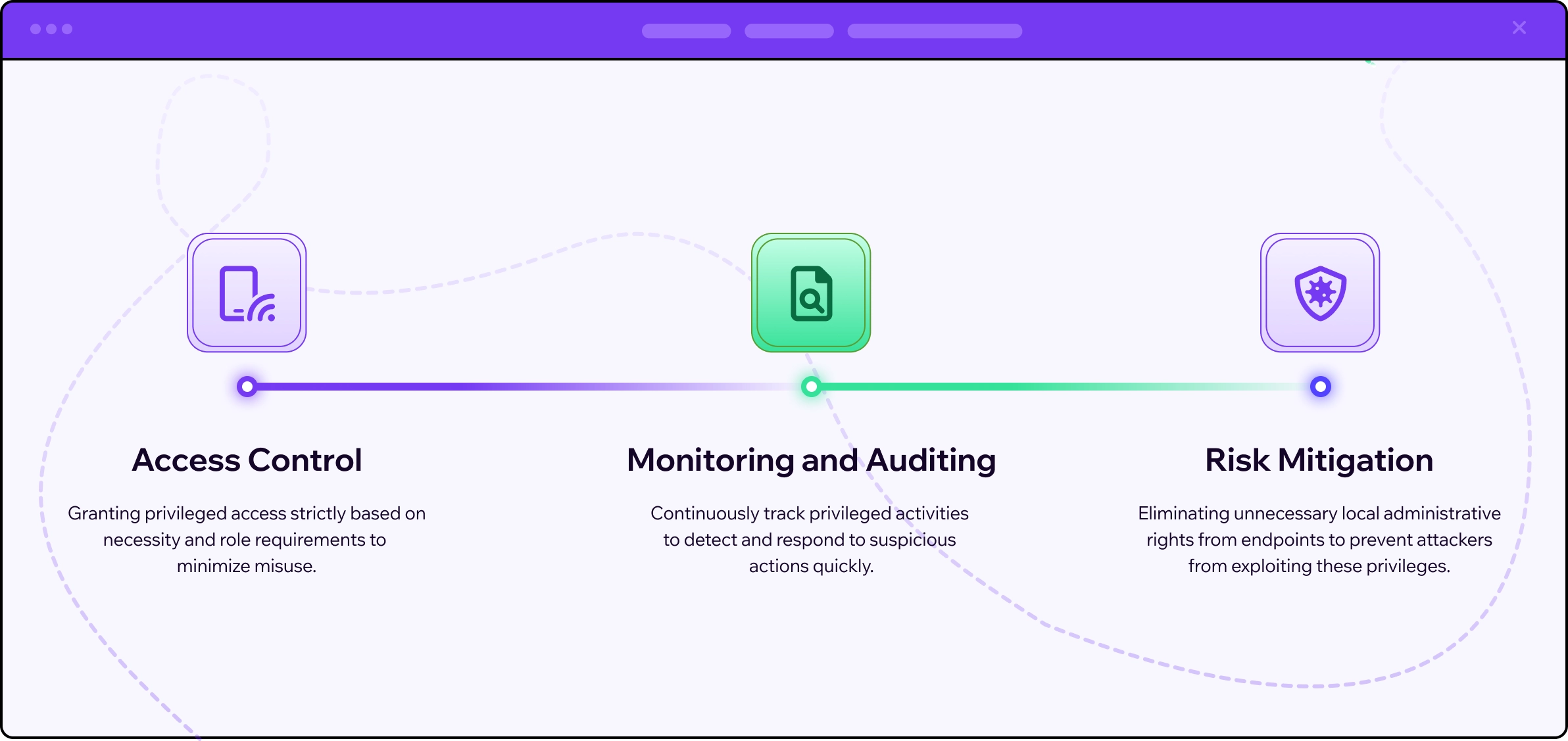
As organizations adopt more complex digital solutions such as cloud services, DevOps, and IoT, the number of privileged access points increases, making PAM even more crucial. Effective PAM helps secure endpoints where attackers can exploit default administrative privileges. By managing these privileges, organizations can prevent lateral movement of threats within the network. Moreover, PAM ensures compliance with regulatory standards by meticulously logging and auditing privileged actions.
Common challenges addressed by PAM
Below are key challenges that most organizations face while managing their privileged accounts:
-
Securing Privileged Credentials:
Managing privileged credentials, which include passwords, SSH keys, and certificates, is critical for overall security. Traditional methods often involve manual rotation and updates, a process prone to errors and inefficiencies. This inefficiency creates significant security risks and operational hurdles for IT teams. Weak credential management practices, like sharing passwords or using weak ones, further amplify these risks.
-
Maintaining Compliance:
Privileged access management (PAM) plays a crucial role in adhering to regulatory standards for data security. However, ensuring ongoing compliance can be challenging. Many industries, such as healthcare (HIPAA) and those in the European Union (GDPR), have strict regulations governing access to sensitive data. This makes it difficult to maintain compliance, especially when managing and monitoring a large number of privileged accounts.
-
Tracking Privileged Activity:
The lack of centralized monitoring and control mechanisms creates a blind spot, leaving privileged user sessions unchecked. This vulnerability exposes them to a double threat: increased risk of security breaches and potential non-compliance with data security regulations.
-
Managing User Experience:
Balancing security with usability is crucial in PAM. Excessively restrictive access controls can hinder productivity and frustrate users, leading to attempts to bypass security measures. Managing security and user experience efficiently can be a difficult task.
-
Protecting Core Infrastructure Components:
Traditional PAM solutions might expose critical infrastructure components, like Windows domain controllers. These systems remain vulnerable to attacks that exploit weaknesses in authentication protocols. This creates a gap in overall security coverage that cybercriminals can exploit.
-
Increasing Cloud Complexity:
The management of privileged access in large organizations is inherently complex, with numerous users, systems, and applications requiring attention. This complexity can hinder the implementation and upkeep of effective Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions. Moreover, overseeing privileged user access across various platforms, including cloud services and SaaS applications, presents substantial compliance risks and operational challenges for organizations.
Top 10 Privileged Access Management Use Cases
To achieve maximum security and ensure continuous compliance for privileged accounts and critical systems, organizations should choose solutions that incorporate the following critical use cases:
Secure & Audit Privileged Account Credentials
Privileged accounts, with their elevated permissions, are prime targets for cyberattacks. To safeguard critical systems and sensitive data, employ a robust approach to securing these accounts:
- Use credential vaulting to store privileged credentials in a secure, encrypted vault, reducing the risk of exposure.
- Implement automated password rotation and management systems to ensure credentials are frequently updated and difficult to compromise.
Additionally, comprehensive audit trails should log detailed privileged access and actions, allowing for monitoring and review. This helps detect anomalies, investigate incidents, and demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements, enhancing security, reducing the risk of credential theft, and improving compliance and accountability.
Implement Application Reputation
Evaluating the reputation of applications requesting privileged access reduces the risk of malware and untrusted software accessing sensitive systems. Use reputation-based controls to whitelist known, trusted applications and block suspicious or unverified ones. This ensures that only safe applications can access privileged resources, enhancing threat detection and response capabilities and providing a more secure and controlled environment.
Control Remote Access
As work-from-home and remote work become the norm, controlling and securing remote access to privileged accounts is more critical than ever. Ensure that remote access is authenticated, authorized, and encrypted to provide a secure connection to sensitive systems. Monitoring and recording remote privileged sessions create a detailed log of actions taken, helping to identify potential misuse and providing crucial evidence for incident response. A secure and controlled remote access approach, combined with the ability to monitor and audit remote sessions, significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Apply PAM Best Practices to Network Devices and IoT/IIoT
Extend PAM best practices to network and IoT/IIoT devices to ensure comprehensive security for all critical infrastructure. Centralize the management of privileged access to streamline operations and enhance security consistency. This approach improves security, simplifies access management, and increases visibility and control over network and IoT/IIoT devices, ensuring a secure and manageable environment.
Secure Kubernetes
Managing privileged access within Kubernetes is essential, and you need to find a platform that is designed to secure containerized applications effectively. Implement granular Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) within Kubernetes to ensure only authorized users and services can perform actions on the cluster, thereby limiting the attack surface. This enhances security for containerized applications, improves access control within Kubernetes clusters, and reduces the risk of compromise in a highly dynamic environment, making securing Kubernetes a vital aspect of your PAM strategies.
Privilege Escalation and Anomaly Detection
Identifying privilege escalation and anomalies is essential for early breach detection and preventing unauthorized access to vital systems. Leverage behavioral analytics to establish standard behavior patterns for privileged accounts and identify deviations that might signal malicious activity. This enables prompt identification of security issues, minimizes insider threat exposure, and enhances incident response with instant alerts, ensuring a proactive approach to safeguarding privileged access.
Streamline Privileged Access Security in the Cloud
Effectively monitor privileged access within cloud environments to safeguard data and services hosted on various cloud platforms. Manage identities, roles, and permissions across diverse cloud services, integrating seamlessly with cloud-native security tools to ensure robust protection and monitoring of privileged activities. This approach strengthens security for cloud infrastructure and services, enables centralized management of privileged access across multi-cloud environments, and enhances compliance with cloud security standards and regulations.
Simplify Compliance Audits
Provide robust audit trails, detailed access logs, and comprehensive reporting features to ensure that all privileged access attempts and actions are carefully recorded for easy review. This clear visibility helps demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices, allowing for confident navigation of audits with transparent management of privileged account activity and adherence to security policies.
Block Lateral and Vertical Movements
Address the critical security challenge of lateral movement, where attackers move from compromised, low-level systems to reach sensitive data on high-value targets. Block these movements using two key strategies:
-
- Robust Access Controls: Implement stringent access controls to restrict user access solely to the essential systems and data.
- Network Segmentation: Segment your network, creating barriers that prevent unauthorized movement between different zones.
This proactive approach helps contain breaches and minimizes damage by stopping attackers from reaching your most critical assets, safeguarding your data and infrastructure from unauthorized access and exploitation.
Secure Third-Party Access
Before granting access, carefully verify external partners’ or vendors’ identities and permissions through granular access controls and authentication mechanisms. This ensures data remains safe from unauthorized access, even if a vendor’s login details are compromised. Establish secure and auditable workflows for third-party interactions, maintaining control over privileged access while fostering collaboration and partnerships.
Conclusion
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is vital for modern cybersecurity. The top 10 use cases outlined here provide effective solutions for securing credentials, controlling access, and ensuring compliance. By implementing these strategies, organizations can strengthen their security and compliance posture, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure secure collaborations.